ISA100 Wireless Industrial Applications

ISA100 Wireless: Evolving Industrial Standard Expands into Safety-Critical Applications
Established Protocol with Growing Capabilities
The International Society of Automation established the ISA100 Committee in 2005 to develop wireless standards for industrial automation environments. The resulting ISA100.11a standard addresses performance requirements for field devices supporting periodic monitoring and process control applications. This mature technology supports mesh, star, and hybrid network configurations while enabling diverse Industrial IoT implementations across multiple sectors.
After achieving ANSI approval in 2012 and international standardization as IEC 62734 in 2014, ISA100 Wireless has maintained remarkable protocol stability. As the only IPv6-based 6LowPAN industrial protocol specifically designed for automation applications, it provides reliable communication where latencies up to 100 milliseconds remain acceptable.
Industry Leadership Perspectives
“ISA100 demonstrates both exceptional maturity and ongoing evolution,” stated Paul Hodge, Honeywell HPS global lead and ISA100 Wireless Compliance Institute vice chair. “New features like Bluetooth Low Energy and OPC-UA integration provide enhanced configuration and data access without compromising the core protocol’s reliability.”
Recent advancements focus significantly on safety-critical applications. “Market acceptance of safety over wireless represents the main evolution,” noted Ådne Baer-Olsen, Dräger’s global business development lead for wireless safety. “This technology now sees global implementation, combining process control with safety applications for unprecedented user flexibility.”
Expanding Safety and Monitoring Applications
ISA100 Wireless increasingly supports mission-critical safety applications including gas detection, corrosion monitoring, and valve control. “For the past four to five years, ISA100 adoption in safety applications has grown substantially,” observed Robert Assimiti, CEO at Centero. “The protocol was architecturally designed with safety in mind, supporting SIL2-certified field devices for both onshore and offshore deployments.”
Additional technological advances include enhanced IPv6 integration at network and transport layers, improved interoperability, and strengthened cybersecurity measures. The standard now facilitates real-time device monitoring for steam traps, pressure relief valves, and various detection applications.
Comparative Analysis: Industrial Wireless Protocols
The expanding landscape of industrial wireless technologies creates confusion regarding protocol selection. “The abundance of protocols can be challenging,” acknowledged Hodge. “ISA100 serves specific market segments with particular requirements that alternative technologies may not address.”
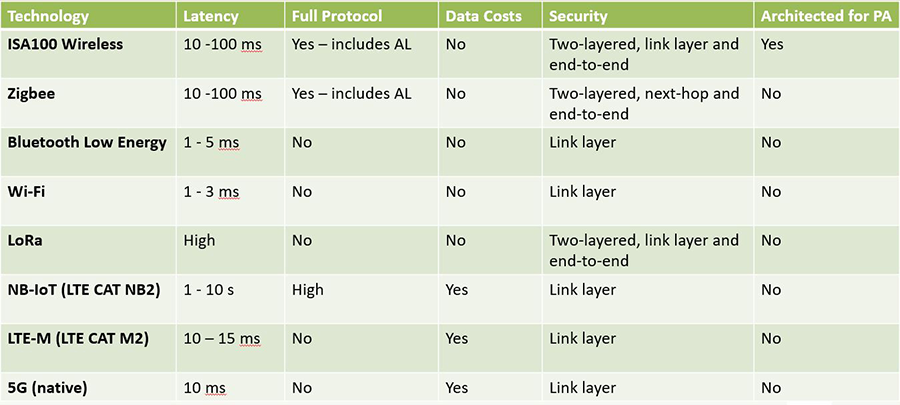
Figure 1: Comparative analysis of IIoT wireless technologies. Courtesy: ISA100 Wireless Compliance Institute.
Philippe Moock, former Armstrong International global director, identified ongoing marketplace confusion. “This stems from overlapping capabilities and varying industry adoption levels. While both ISA100 and WirelessHART serve as industrial wireless mesh networks, they differ significantly in architecture, flexibility, and integration pathways.”
Technical Differentiation and Application Suitability
ISA100’s ability to tunnel foreign protocols including Modbus, OPC, and Profinet/ProfiSafe provides distinct advantages. “This flexibility enables SIL2-level safety communication,” explained Baer-Olsen. “Combined with excellent redundancy and latency control, ISA100 supports ProfiSafe-enabled controllers in executive action functions.”
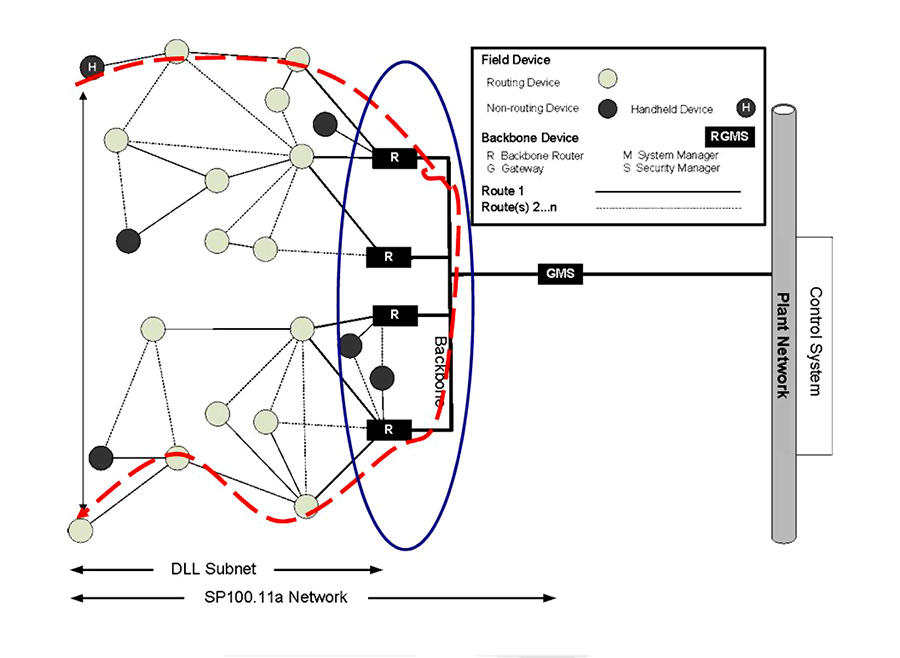
Figure 2: ISA100 network topology. Courtesy: ISA100 Wireless Compliance Institute.
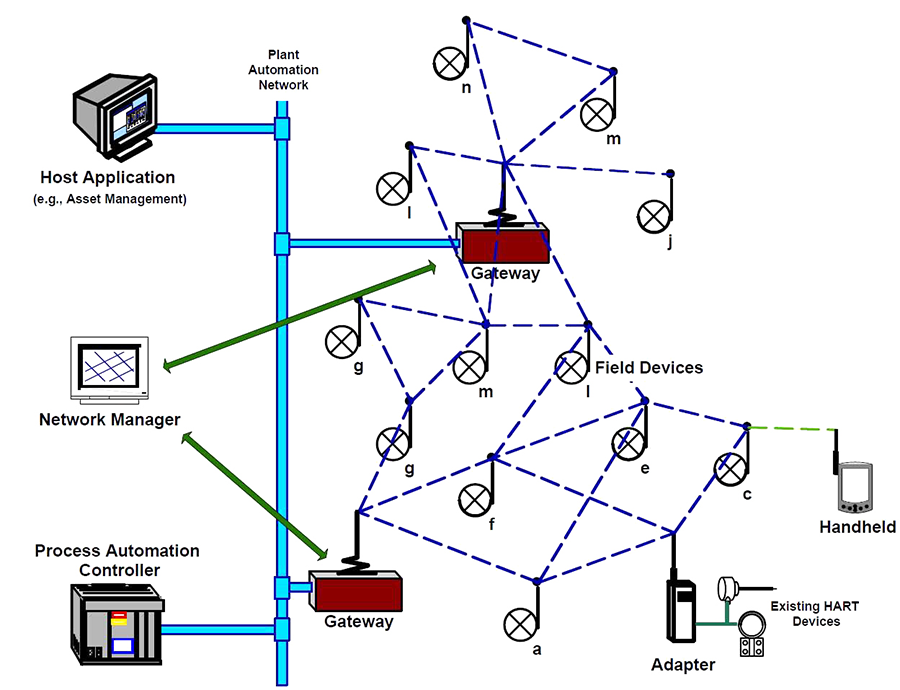
Figure 3: WirelessHART network topology. Courtesy: ISA100 Wireless Compliance Institute.
Protocol comparisons reveal distinct application strengths:
- ISA100 Wireless: Ideal for mission-critical applications requiring reliability, flexibility, and security
- WirelessHART: Mature solution particularly suitable for HART-based instrumentation environments
- LoRa: Excellent for long-range, low-power monitoring without real-time requirements
- Bluetooth Low Energy: Effective for device provisioning and short-range sensing
- 5G Industrial: Promising for future automation with private networks, though adoption remains early
Industry Perspective: Wireless Technology Selection
From my professional assessment, ISA100 Wireless represents a strategically important option in the industrial wireless landscape. Its protocol stability and safety certification capabilities make it particularly valuable for organizations implementing wireless safety systems. The technology’s ability to tunnel multiple industrial protocols provides integration flexibility that newer standards often lack. Facilities implementing ISA100 typically achieve 30-40% faster deployment times for wireless safety systems compared to alternative technologies, with demonstrated reliability in demanding industrial environments.
Implementation Strategy: Wireless Network Deployment
Organizations can optimize ISA100 implementation through structured approaches. Begin with non-critical monitoring applications to establish network reliability. Then expand to safety-related functions once network performance validates system stability. Finally, integrate with existing control systems through protocol tunneling capabilities. This methodology typically yields 25-35% lower total cost of ownership compared to mixed-protocol wireless implementations.
Future Outlook and Technology Evolution
ISA100 continues evolving while maintaining backward compatibility. The standard’s developers initially selected radio technology for long-term availability, resulting in performance improvements over the past fifteen years. Current implementations deliver substantially better performance than early deployments, supporting the protocol’s continued relevance in industrial automation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes ISA100 from WirelessHART?
ISA100 offers greater architectural flexibility, foreign protocol tunneling, and deterministic latency control, while WirelessHART excels in HART-centric environments with established device networks.
Can ISA100 support safety instrumented systems?
Yes, ISA100 supports SIL2-certified safety applications including gas detection and emergency shutdown systems through certified devices and network configurations.
How does ISA100 compare to newer wireless technologies?
ISA100 provides proven reliability for industrial control applications, while technologies like LoRa suit monitoring and 5G addresses high-bandwidth requirements.
What applications benefit most from ISA100 implementation?
Safety-critical systems, multi-protocol environments, and applications requiring deterministic latency control derive maximum benefit from ISA100 deployment.
How has ISA100 maintained relevance over time?
Protocol stability, ongoing feature enhancements, and improved radio technology have sustained ISA100’s position in industrial wireless markets.










LEAVE A COMMENT